In the rapidly evolving digital ecosystem, SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is no longer just about keywords and backlinks. With Google’s continuous advancements in natural language understanding and user intent interpretation, businesses—especially in the United States—must adapt to stay competitive. Two major approaches dominate today’s SEO landscape:
- Traditional SEO
- Semantic SEO
This comprehensive guide explains both, explores key differences, and provides actionable strategies U.S. businesses can implement to rank higher, attract quality traffic, and align with Google’s latest updates.
What Is Traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO focuses on optimizing web pages based on keywords, backlinks, and on-page elements such as title tags and meta descriptions.
Core Components Of Traditional SEO
- Keyword Optimization: Target specific terms users type into search engines.
- On-page SEO: Optimize meta tags, headers, URLs, and content structure.
- Off-page SEO: Build backlinks from authoritative websites.
- Technical SEO: Improve site speed, crawlability, and indexation.
Purpose Of Traditional SEO
Traditional SEO helped search engines match keywords on your site with queries users entered. It was effective in an era where Google and others relied heavily on surface-level text matching.
What Is Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO goes beyond exact-match keywords. It focuses on search intent, context, and conceptual relevance of content.
Semantic SEO uses:
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords
- Topic clusters
- Structured data/Rich snippets
- User intent optimization
Why Semantic SEO Matters
Google’s algorithms—like BERT, RankBrain, and the latest MUM updates—understand search queries similar to human language processing. They now interpret:
- Context
- Synonyms
- Related concepts
- User goals (informational, navigational, transactional)
Semantic SEO ensures your content answers why and how, not just what.

Semantic SEO Vs Traditional SEO: Side By Side
| Feature | Traditional SEO | Semantic SEO |
| Keyword Focus | Exact-match keywords | Search intent & topical relevance |
| Scope | Page-level | Topic-level clusters |
| Ranking Signals | Backlinks & keywords | User intent + context + structured data |
| Content Strategy | Individual pages | Thematic authority |
| User Experience | Lower emphasis | High emphasis |
Why U.S Businesses Must Embrace Semantic SEO
Google’s AI-first indexing prioritizes relevance over repetition. Simply stuffing keywords won’t work anymore.
Key Benefits Of Semantic SEO
- Better Visibility For Rich Snippets & Knowledge Panels
Structured data and contextual content make it easier for Google to surface your content as a featured snippet. - Improved User Engagement
Answers user intent more effectively, reducing bounce rates and increasing time on page—two signals Google values. - Higher Conversion Rates
Content tailored to user intent aligns more closely with what buyers seek, resulting in higher engagement and conversions. - Topic Authority And Trust
Covering related subtopics builds your site’s authority and signals expertise to search engines.
Google’s Latest SEO Guidelines
Google’s most recent updates emphasize:
- Helpful Content: Content that prioritizes users over search engines.
- Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T)
This expands on the older E-A-T framework by adding experience—meaning showing real-life use, case studies, or personal insights. - Semantic Intent Matching
Google identifies synonyms, related phrases, and context nodes to interpret meaning—not just word form.
To thrive in this year and beyond, your SEO strategy must satisfy these criteria.
How To Implement Semantic SEO: Step-By-Step
1. Start With Intent-Based Keyword Research
Instead of just targeting high-volume keywords, break them into three intent types:
- Informational: “What is semantic SEO?”
- Navigational: “Semantic SEO tools”
- Transactional: “Hire semantic SEO services”
Use tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to identify user intent signals.
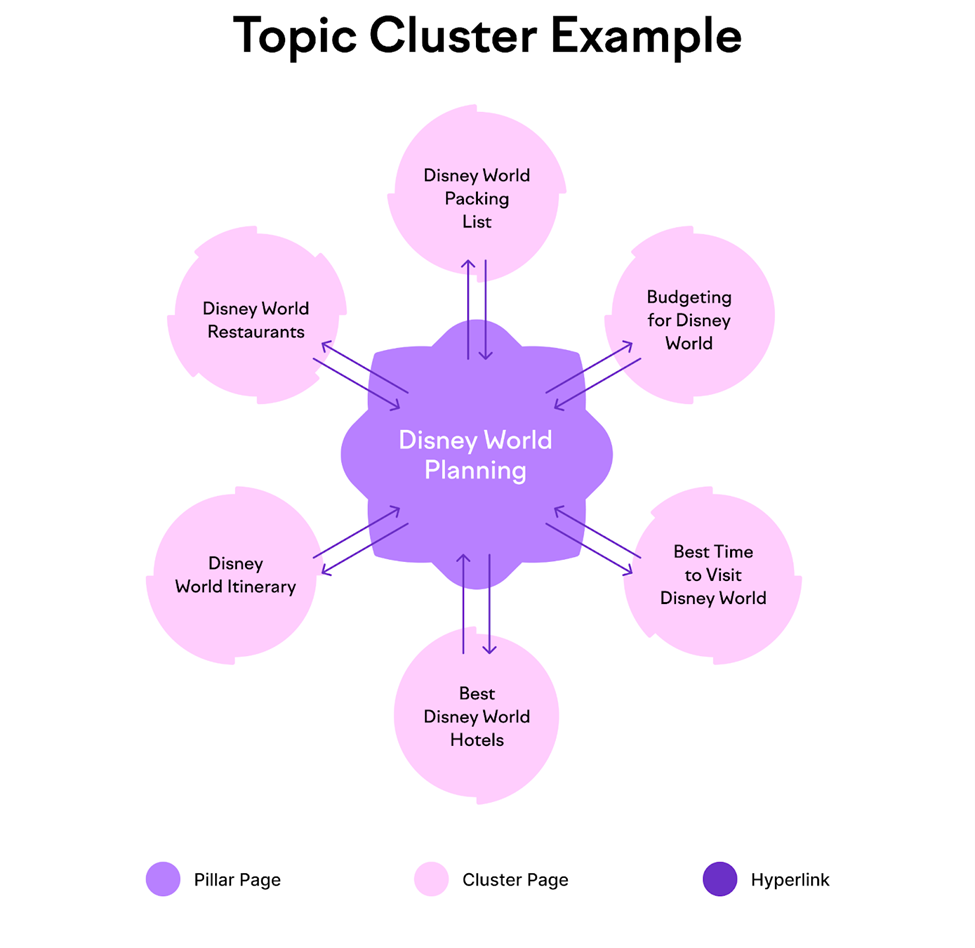
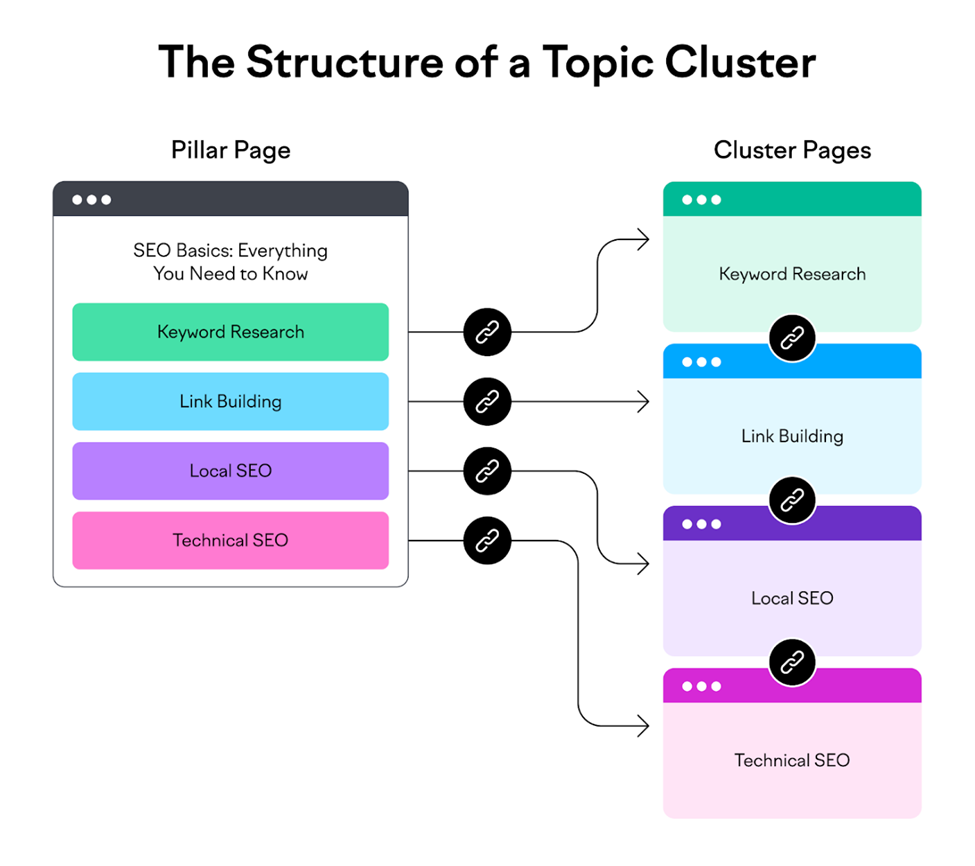
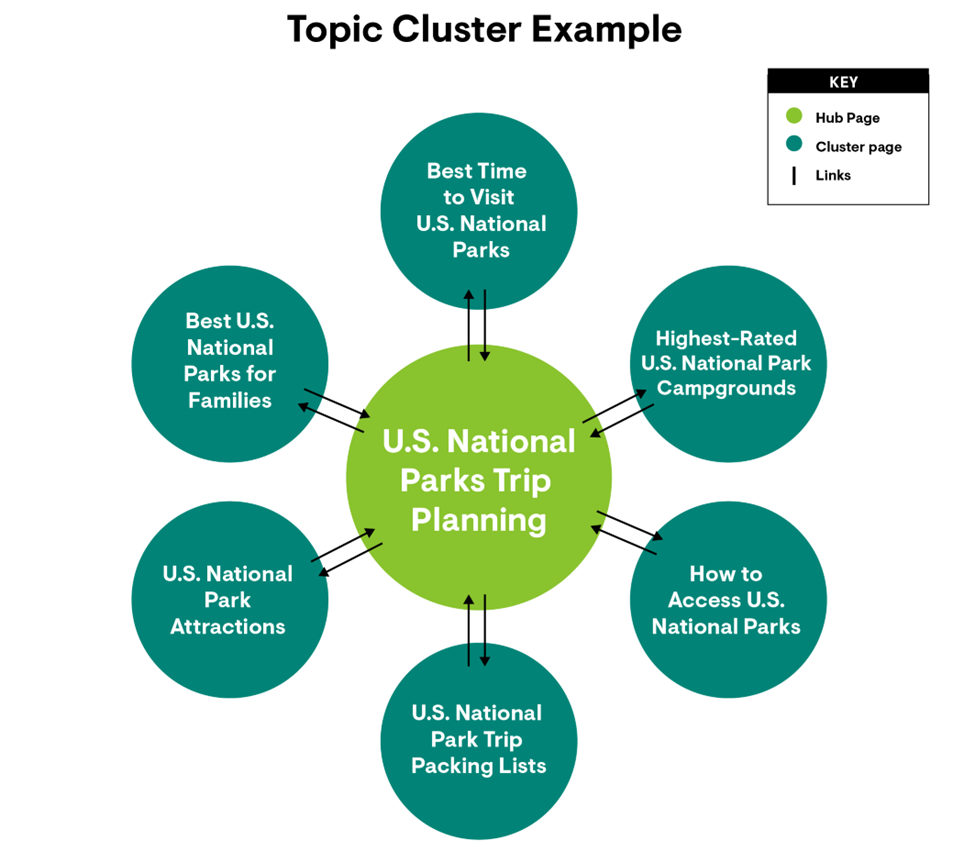
2. Create Topic Clusters
A Topic Cluster consists of:
- Pillar Page: Covers a broad topic comprehensively.
- Cluster Content: Supports the pillar with related subtopics.
This creates semantic relationships between pages, improving relevance in Google’s understanding.
Example:
- Pillar: Ultimate Guide to Semantic SEO
- Cluster 1: Semantic Keywords vs LSI Keywords
- Cluster 2: How to Use Structured Data
- Cluster 3: Semantic SEO Tools for eCommerce
3. Use Structured Data
Structured data helps search engines interpret your content’s meaning and purpose. This can enhance search listings through:
- Rich snippets
- Knowledge panels
- Breadcrumbs
- Product/Review schema
Examples of schema types:
- Article
- FAQ
- Product
- Organization
- Local Business
4. Optimize for Featured Snippets & People Also Ask
Semantic SEO increases visibility in:
- Featured snippets
- People Also Ask (PAA) boxes
- Knowledge Graph results
Tips:
- Use question-based subheadings
- Answer queries concisely (40–60 words)
- Add tables, lists, and bullets
5. Improve Internal Linking Patterns
Linking supports semantic relevance:
- Link cluster content to pillar pages
- Use descriptive anchor text
- Avoid over-optimization
This tells Google which pages are conceptually related.
6. Write With Natural Language
Create human-first content that reads naturally. Avoid:
- Keyword stuffing
- Repetitive phrases
- Thin or irrelevant content
Instead, aim for:
- Clarity
- Depth
- Conversational tone
Supports Google’s Helpful Content Update and experience-first ranking.
Semantic SEO Metrics That MatterTraditional metrics are still relevant, but Semantic SEO adds new performance indicators:
| Metric | Why It Matters |
| SERP Position | Still important, but not the only goal |
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Measures snippet relevance |
| Bounce Rate & Dwell Time | Indicates content relevance |
| Topic Authority | Number of semantically related pages ranking |
| Featured Snippet Wins | Shows trust by Google in your content |
Tracking these helps refine your semantic strategy.
Tools That Help With Semantic SEO
Here are some categories:
Keyword & Topic Research
- SEMrush
- Ahrefs
- Surfer SEO
Semantic Optimization Tools
- Clearscope
- MarketMuse
- Frase
Analytics & Reporting
- Google Analytics
- Google Search Console
These tools help you build semantically rich content grounded in search intent.
Traditional SEO Still Matters-But It’s Not Enough
Traditional SEO lays the foundation: site structure, mobile responsiveness, backlinks, and technical SEO are critical. However, semantic SEO amplifies and future-proofs your strategy by aligning with user intent and context.
Think of Traditional SEO as “building a house”
Semantic SEO is “designing the interior for user experience and flow.”
You need both.
Semantic SEO Best Practices Checklist
- Map keywords to user intent
- Create topic clusters
- Use schema markup
- Optimize for rich results
- Improve internal linking
- Update outdated content
- Write user-first (not bot-first) content
Final Takeaway For U.S Businesses
Semantic SEO is no longer optional—it’s essential. With Google’s AI-powered algorithms and evolving expectations for user experience, businesses must prioritize relevance, intent, and depth of content.
By adopting a semantic approach, U.S. companies can:
- Increase visibility in competitive niches
- Attract qualified organic traffic
- Enhance user engagement and conversions
- Build long-term topical authority
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s The Biggest Difference Between Semantic And Traditional SEO?
Semantic SEO prioritizes intent and context, while traditional SEO focuses on keyword matching. Semantic SEO aims to answer questions users didn’t even know how to ask, whereas traditional SEO targets exact search phrases.
Do I Still Need Backlinks In Semantic SEO?
Yes. Backlinks remain a powerful trust signal. Semantic SEO complements this by building contextually relevant content that earns better links and enhances topical authority.
How Long Does It Take To See Results From Semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is a long-term strategy. Depending on competition and your current SEO health, measurable improvements may appear between 3 to 6 months, with stronger authority gains over 6–12 months.
